HAE Management
HAE is an unpredictable and potentially life-threatening genetic disease1
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a rare genetic disease that causes recurrent, debilitating, and potentially life-threatening attacks of angioedema in the body. HAE affects about 1 in 50,000 people of all ages.2,3
An accurate and early diagnosis is an important first step in developing an effective management plan for your patients with HAE. The frequency and severity of HAE attacks may vary for each individual over time regardless of age, meaning past attacks do not predict the severity of future attacks.5
HAE laryngeal attacks can be life-threatening, and they are especially dangerous for children who lack the ability to self-administer treatment during an attack or who may be unable to describe their symptoms.4,6
TAKHZYRO is not indicated for acute treatment.
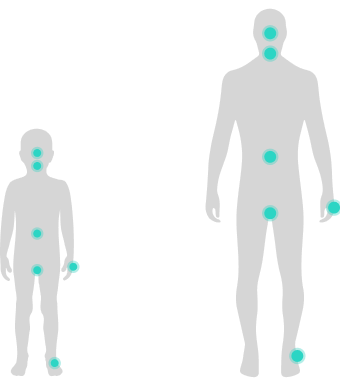
For both adult and pediatric patients, attacks can occur in the…4
- FACE
- LARYNX
- ABDOMEN
- GENITALS
- HANDS
- FEET
Craft an effective HAE management plan7
Long-term HAE prevention should be individualized and considered in all patients with HAE7
Ask yourself the following questions to help understand the signs of a patient who is trigger avoidant with a low attack history
- Does your patient experience HAE swells in their extremities, but not classify them as attacks?
- Does your patient avoid activities because of their HAE?
- Would your patient live their life differently if they were on a preventive treatment?
Your patients’ needs and disease may change over time, and they may need a reminder that their management plan can change.2
- All patients with HAE should have access to at least 2 doses of an acute medication in order to treat attacks when they happen2
- The 2020 US HAEA guidelines recommend:
- Reviewing management plans for patients with HAE on a regular basis, including the need for preventive treatment2
- TAKHZYRO as one of the first-line therapies for long-term prevention in adult and adolescent patients ≥12 years of age2
HAEA=Hereditary Angioedema Association.
Since most attacks are unpredictable and not prompted by triggers, the 2021 international WAO/EAACI guidelines suggest physicians should not support excessive avoidance of suspected triggers, which can limit a patient’s normal life.7
- High HAE disease activity and other factors often comes with impact on daily life7
- The daily lives of some patients with low attack rates are also impacted, thought to be linked to the unpredictability and continuous fear of HAE attacks7
EAACI=European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology; WAO=World Allergy Organization.
Long-term HAE management
Watch as 2 HAE experts break down best practices used by doctors to understand the impact of HAE, as well as to create long-term HAE management plans for their patients.

Dr Cristina Ramos: Thank you.
Dr Daniel Soteres: Delicious. Thanks.
Dr Cristina Ramos: So Danny, I just had an interesting conversation with one of my patients with HAE that I think you can relate to. This patient has been resistant to preventive therapy for a while. She's been downplaying her HAE attacks saying things like, "Oh, it's just a hand swell, no big deal."
Dr Daniel Soteres: Ah, yes, this sounds familiar.
Dr Cristina Ramos: But today, she came in with her husband and he said she was having attacks every week. She finally realized the impact HAE was having on her and her family and decided to start preventive treatment. For the longest time, she had minimized her condition.
Dr Daniel Soteres: I have patients who may have attacks that impact their daily lives. One patient of mine is a waitress. She had a hand swell one time during work. Imagine her job that day. Serving food, clearing tables with a hand swell. She downplayed the attack, but I knew it was affecting her. I let her know it was very helpful that she told me about it, because it clarified to me that she could likely benefit from preventive therapy. I didn't want her to downplay the discomfort she was experiencing, and I didn't want her normalizing an attack that would cause her to miss a day of work. Many patients make sacrifices they don't have to.
Dr Cristina Ramos: I agree. It's important for us to understand how HAE affects patients' daily activities. We shouldn't just ask, "When was the last time you had an attack?" We also need to ask, "Did you miss something important due to an HAE attack?" That helps patients consider how much the disease may be affecting them and whether we need to explore another treatment approach.
Dr Daniel Soteres: Exactly. Tracking how often they use acute treatment is also beneficial. One of my patients kept a log for a year. But this isn't something most patients will do. I ask them at clinic appointments, sit back, reflect on their attacks over the past few months. I give them a pen, piece of paper, and a calendar, and I leave them alone while I see another patient, come back a few minutes later to see what they've come up with.
Dr Cristina Ramos: That's a really helpful way to have patients think about their attack history. How do you approach patients when they're first diagnosed with HAE?
Dr Daniel Soteres: Well, for newer patients, it's important not to pressure them into making treatment decisions at the first visit. HAE is a lifelong disease, and I want patients to know that I'm invested in being a guide for them throughout that whole journey.
Dr Cristina Ramos: Yes, definitely. Checking in every few months is essential when establishing a long-term management plan. I've seen that some patients will consider prevention when their attacks increase, but others don't. Perhaps they worry it will interfere with their daily routines?
Dr Daniel Soteres: That's why we need to balance conversations about treatment options with patients' personal concerns and their health literacy. I treat patients of all ages, children, adolescents, and adults through our understanding of the disease. And their options are quite different and they change over time.
Dr Cristina Ramos: Sometimes I ask, "Do you prefer an injection that you can administer every couple of weeks? Or do you want to take something every day?" Above all, patients need to feel comfortable with their choices.
Dr Daniel Soteres: Ooh, I really like that approach. You mind if I use it in my practice?
Dr Cristina Ramos: Not at all, Danny. And I think I'm going to use the tracking method you mentioned also.
Dr Daniel Soteres: I discuss all the options with my patients and try to take into consideration their goals and perspectives. When it comes to TAKHZYRO, from my experience, patients get started on it and after a period of time they see results. I don't have too many patients calling after several months and saying, "I'm having frequent attacks."
Dr Cristina Ramos: You know, I recognize these are individual patient experiences, and every patient's experience is different. TAKHZYRO has been studied in the broadest range of patients age two years and older. And I found that many of my patients have seen a decrease in their HAE attacks, including patients with an infrequent attack history.
Dr Daniel Soteres: I appreciate that my patients don't let their HAE define them. My experience prescribing TAKHZYRO in my practice has shown positive results for them. Reaching steady state within the first few months is something I explain to my patients when they begin treatment to set expectations. I always tell patients that breakthrough attacks can happen, but it's important to stick with their dosing schedule. And they do, even when they go on camping trips or vacations. Treating patients every two or four weeks can give them back their time.
Dr Cristina Ramos: Which is why every two- or four-week dosing can be a plus for patients.
Dr Daniel Soteres: Adult patients are not the only ones who should consider preventive therapy. One of my 13-year-old patients saw enough of a reduction in attacks after starting on TAKHZYRO that her mother felt more comfortable to consider sending her to another state to perform with the school orchestra. And of course, the three of us all discussed the potential risks of TAKHZYRO, including the most common side effects.
Dr Cristina Ramos: Also, thanks to the expanded indication, we can offer TAKHZYRO to patients from 2 to less than 12 years of age.
Dr Daniel Soteres: Patient experiences like these help me feel like I'm supporting my patients as best I can.
Dr Cristina Ramos: I completely agree. When I see older patients with HAE who haven't had access to preventive treatment for part of their lives, it's so satisfying to be able to provide a treatment option like TAKHZYRO.
Dr Daniel Soteres: Yes, and it's also nice to know that TAKHZYRO is the number one prescribed HAE preventive treatment.
Dr Cristina Ramos: Danny, this was helpful. Thanks for catching up with me today.
Dr Daniel Soteres: Of course. Let's make a plan to talk like this more often.
Narrator: TAKHZYRO (lanadelumab-flyo) is indicated for prophylaxis to prevent attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in patients ≥2 years of age.
Hypersensitivity reactions have been observed. In case of a severe hypersensitivity reaction, discontinue TAKHZYRO administration and institute appropriate treatment.
Adverse Reactions: The most commonly observed adverse reactions (≥10%) associated with TAKHZYRO were injection site reactions consisting mainly of pain, erythema, and bruising at the injection site; upper respiratory infection; headache; rash; dizziness; diarrhea; and myalgia. Less common adverse reactions observed included elevated levels of transaminases; one patient discontinued the trial for elevated transaminases.
Use in Specific Populations: The safety and efficacy of TAKHZYRO in pediatric patients <2 years of age have not been established.
No data are available on TAKHZYRO in pregnant women. No data are available on the presence of lanadelumab in human milk or its effects on breastfed infants or milk production.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Dyax Corp., a Takeda company, at 1-877-TAKEDA-7 (1-877-825-3327), or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Please see full Prescribing Information at TAKHZYRO.com/hcp.
Efficacy and safety data across multiple studies
Explore the results and see what this could mean for your patients
Enroll your patients
Complete the digital enrollment form today or download the form to fax
References: 1. Banerji A, Bernstein JA, Johnston DT, et al. Allergy. 2022;77:979–990. doi.org/10.1111/all.15011 2. Busse PJ, Christiansen SC, Riedl MA, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9(1):132-150.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2020.08.046 3. Banerji A. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013;111(5):329-336. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2020.08.046 4. Zuraw BL. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(10):1027-1036. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp0803977 5. Bork K, Davis-Lorton M. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;45(1):7-16. 6. Johnston DT, Smith RC. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2020;41(6)(suppl 1):S43-S46. doi:10.2500/aap.2020.41.200042 7. Maurer M, Magerl M, Betschel S, et al. Allergy. 2022;77(7):1961-1990. doi:10.1111/all.15214 8. Takhzyro. Prescribing information. Dyax Corp; 2025.
